What is osteoarthritis?
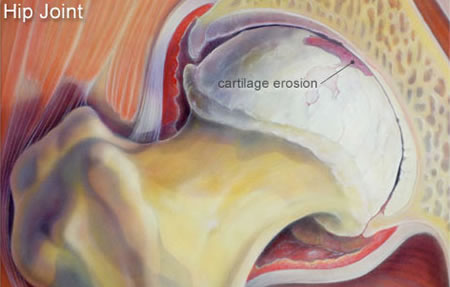
Arthritis is a general term that means ‘joint inflammation’. Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of arthritis. It occurs when the cartilage covering the end of the bones thins and eventually wears away—leading to pain as the bones rub against each other. Inflammation usually accompanies cartilage breakdown and contributes to pain and disability.
What causes osteoarthritis?
In most cases of OA, the specific cause of a disease is not known. However, certain factors may increase the risk of developing OA. Some of these risk factors include heredity, advanced age, obesity, joint injury or joint overuse.
What joints does osteoarthritis affect?
OA can occur in any joint, but most often affects the hands and weight-bearing joints such as the hips, knees, and in the spine. OA of the hip and knee are the most debilitating forms of the disease.
Is osteoarthritis common?
Yes. In fact, OA is the most common joint disease in the world. The WHO (World Health Organization) estimates that about 10% of the world’s population over 60 years of age has 0A.
Who does osteoarthritis affect?
OA affects people of all ethnic groups in all geographic locations. Elderly people are especially affected by OA. After the age of 40, the incidence of OA increases rapidly with each passing decade in all joints. This is likely due to an accumulated exposure to various risk factors, such as weight gain and joint stress. In addition, after the age of 50, OA affects more women than men, and women are more likely to have severe OA as well.
What are the symptoms of osteoarthritis?
Common symptoms of OA include:
- Joint pain during or after use, or after a period of inactivity
- Joint tenderness, stiffness, or sometimes swelling
- Bony enlargements in the middle and end joints of the fingers
These symptoms of OA tend to develop gradually and may get worse over time.
How does osteoarthritis impact the lives of those affected?
OA may affect life in 2 ways:
- First, the pain associated with OA may impact the quality of life, as it can reduce mobility, thereby impairing the ability to work and limiting the daily activities.
- Second, OA may affect mental health. Living with pain and disability can cause prolonged stress, negatively affecting emotional health and well-being.
How is osteoarthritis diagnosed?
In addition to assessing joint pain and mobility impairment, doctors may also use X-rays to help diagnose OA. X-rays can reveal if and how much cartilage has been lost from the affected joint(s). Sometimes blood tests are also done to rule out other forms of arthritis.
How is osteoarthritis treated?
Although there is no known cure for OA, the available treatments can help to reduce pain and improve joint function. Currently, there are 4 types of treatment strategies:
- Education and lifestyle changes: Recommended as the first line, they include weight reduction, pain management strategies, exercise, physical therapy and/or walking aids.
- Medication: To decrease joint inflammation and pain; may include creams, pills, or injections directly into the affected joint(s). Common oral medication includes fast-acting anti-inflammatory drugs such as paracetamol and Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen.
- Food supplement: To relieve OA pain and help improve joint function over the long-term. They also help to lessen the use of anti-inflammatory medications that can cause the risk of gastrointestinal side effects. You may want to learn here on how Arthaffect® can help to repair and restore existing joint tissues.
- Surgery: Reserved for the most severe cases (e.g. joint replacement).
How do fast acting anti-inflammatory drugs work?
As their name implies, these drugs are used for immediate relief from pain and inflammation in the joints. Although they help to control pain and improve function in the short-term, they are associated with gastrointestinal (GI) distress, such as upset stomach, cramping, diarrhea, ulcers and even bleeding. Newer types of NSAIDs, called COX-2 selective inhibitors, are associated with fewer GI side effects but do increase the risk for cardiovascular disease.
Best,
Tan Kok Hui
Nutrition Made Simple, Life Made Rich